It’s Time To Celebrate Dark Matter!
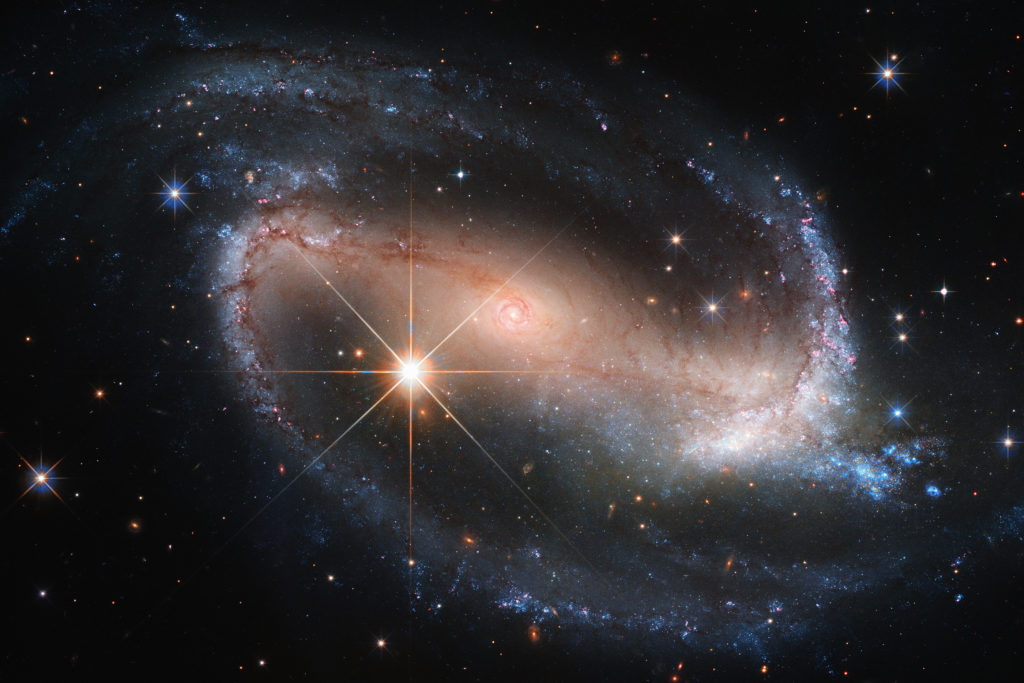

When you think of outer space, you probably think of planets, moons, and stars. But much of our universe is made of dark matter — that is, matter that cannot be observed. While we can’t see dark matter, it can be detected through its gravity-based effects in space, according to the Dark Matter Day website.
While we know dark matter exists, scientists still aren’t quite sure what it is. Whatever it is, scientists think it makes up a big chunk of our universe — about a quarter of its total mass. Some scientists think dark matter isn’t matter at all. It could contain particles they have yet to discover, or perhaps the laws of physics are not yet developed enough to give us the whole picture of our universe. Either way, there’s still a lot about our universe that remains a mystery.
Scientists also believe another mysterious force known as “dark energy” makes up 68.3 percent of the universe. While dark energy is a complete mystery, it is believed to be the driving force behind the universe’s expansion. A possible explanation — based on a version of Albert Einstein’s theory of gravity — is that empty space contains its own energy, according to NASA.
“Because this energy is a property of space itself, it would not be diluted as space expands,” explains the agency on its website. “As more space comes into existence, more of this energy-of-space would appear. As a result, this form of energy would cause the universe to expand faster and faster.”
While dark matter and dark energy present many conundrums, it’s very important that scientists figure it out, since it would help us understand the nature and history of our universe.
Want to learn more about dark matter? Celebrate Dark Matter Day!
Dark matter day has plenty of virtual and in-person events scheduled this year. Check out the event schedule to sign up.